4 new super contribution opportunities
For older Australians, it has been more difficult to build up their superannuation balances. Once you are 67 years of age, there is a requirement to meet a ‘work test’ in order to continue to contribute. This work test forced you to work 40 hours over 30 consecutive days in order for you to make a lump sum contribution (known as a non-concessional contribution) of up to $110,000.
With these restrictions, it was important to carefully plan your superannuation strategy from a younger age.
However, the Federal Government sought to amend these restrictions.
May 2021 Federal Budget
In the May 2021 Federal Budget, the government announced a number of initiatives to assist Australians in building up their superannuation.
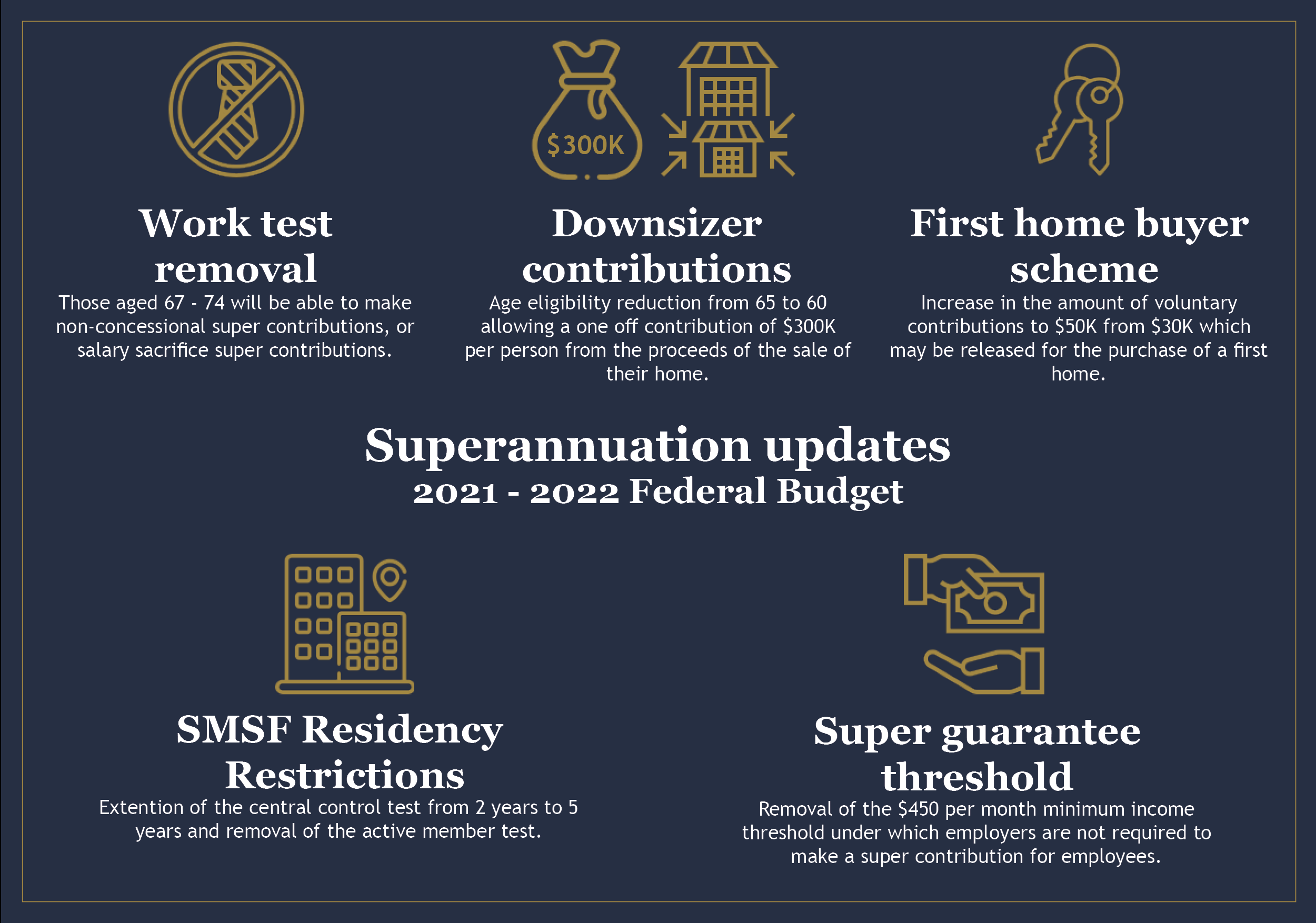
These included:
- Removal of $450 monthly income threshold for super contributions.
- Reduction in age to 60 for the downsizer contributions.
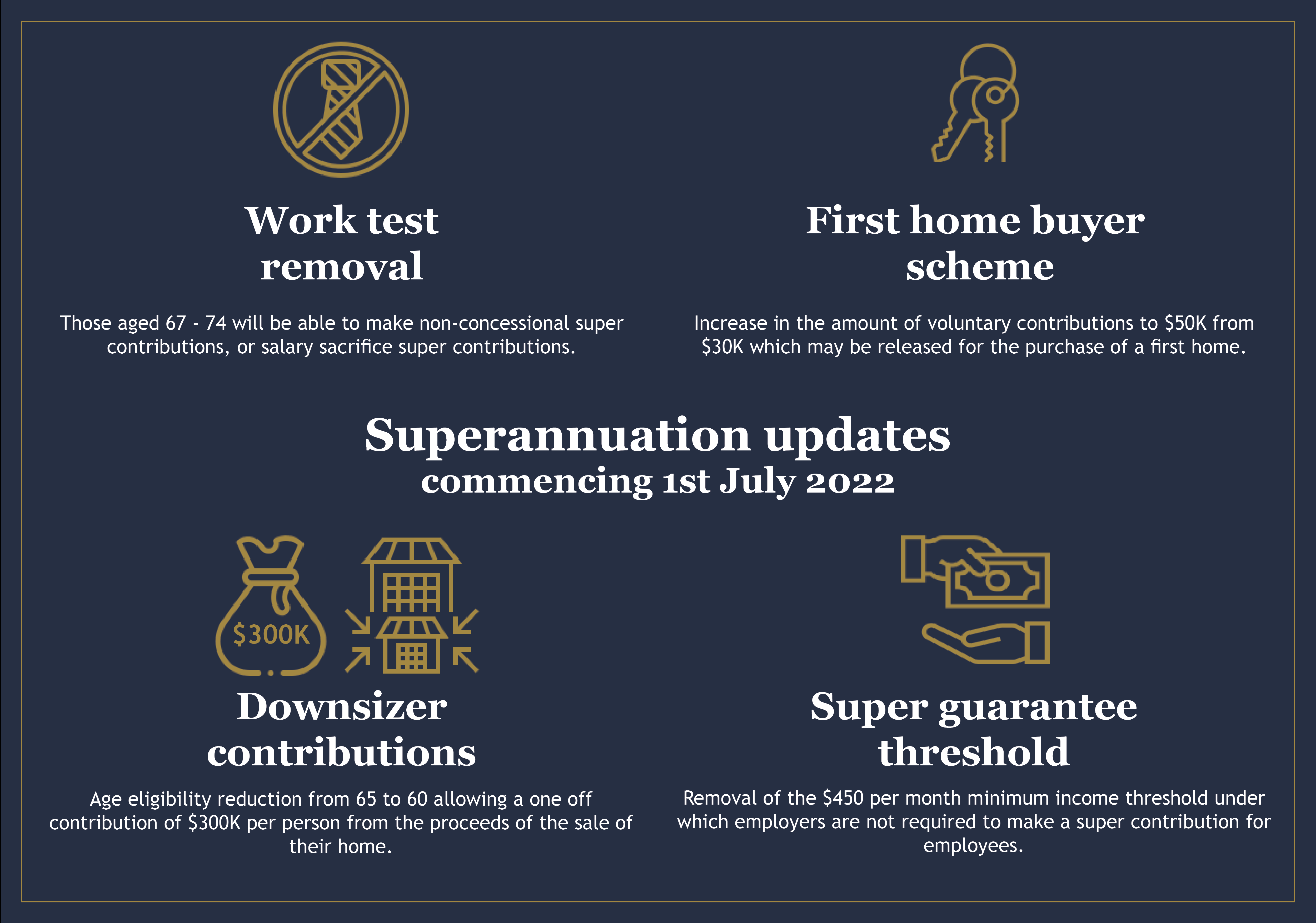
- Removal of the work test for people aged 67-74.
It also increased the withdrawal limit for First Home Super Saver Scheme (FHSS).
Legislation has now passed both houses of parliament and will apply form 1 July 2022.
Removal of $450 monthly income threshold
The government has finally scrapped the $450 superannuation guarantee threshold. This should make approximately 300,000 people eligible for super contributions from 1 July 2022.
Lower Age for ‘Downsizer’ contributions
In selling the family home, couples have the ability to contribute $300,000 each into superannuation as a personal contribution. The age for this contribution was 65, however, it has been lowered to 60. As of May 2021, 22,000 Australians have taken advantage of this opportunity to boost their retirement balances. It should also be noted that these contributions are not restricted by the $1.7m transfer balance cap.
The lowering of age to 60 will come into effect from 1 July 2022.
First Home Super Save increased capacity
This is a great opportunity for couples who are saving for their first home. This scheme allows people to make voluntary contributions to superannuation to save for this purchase. The current caps on these contributions are $15,000 a year and $30,000 in total.
However, it has been passed to allow voluntary contributions (both post tax or through salary sacrifice) up to $50,000 in total.
So a couple will have access to $100,000. It’s important to remember compulsory employer contributions are excluded. Only voluntary contributions may be withdrawn.
This will commence from 1 July 2022.
Removal of work test for 67-74 year olds
The most significant superannuation opportunity announced in the May 2021 Federal Budget was to allow 67-74 year olds to make a personal contribution to superannuation without meeting the current work test. This has now been passed and will come into affect on 1 July 2022.
However, not only will older Australians be able to make a personal contribution of $110,000 pa, but they will also be able to take advantage of the bring forward rule and contribute $330,000 as a lump sum.