Contrarian investing is always difficult because, by definition, it requires swimming against the tide, which can be uncomfortable and tiring. While it’s certainly not for everyone, it is often where the best value and opportunity is to be found. Small cap companies in Australia and the United States may well be offering that opportunity right now.
Since the Australian share market peaked back in August 2021, the Small Ordinaries Index (XSO) has copped a way harder beating than its large cap peers falling by more than 20 per cent over the course of the market correction, while the ASX100, made up of the 100 largest companies on the Australian stock exchange, has dropped by only 5 per cent.
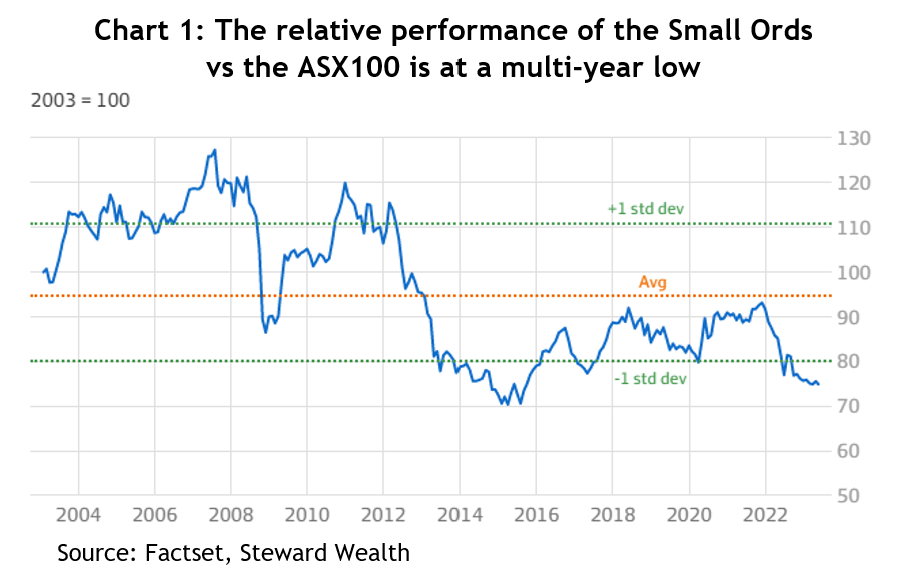
For a bit of longer-term perspective, the returns from XSO relative to the top 100 stocks is more than 20 per cent below its 20-year average, or more than 1.5 standard deviations. That is only 5 per cent away from its lowest level in at least the last 30 years – see chart 1.
Similarly, the Russell 2000 (R2K) index of US small cap stocks has taken a similar beating during this market correction and is still down 22 per cent from the market’s high at the end of 2021. After tracking the large cap S&P500 for most of that time, over the past two months the performance gap is now the widest it’s been over that 17-month period.
Again, however, for some longer-term perspective, after the recent AI-driven rally in the mega cap tech stocks, the R2K’s returns relative to the S&P500 is about 27 per cent, or almost two standard deviations, below its 20-year average.
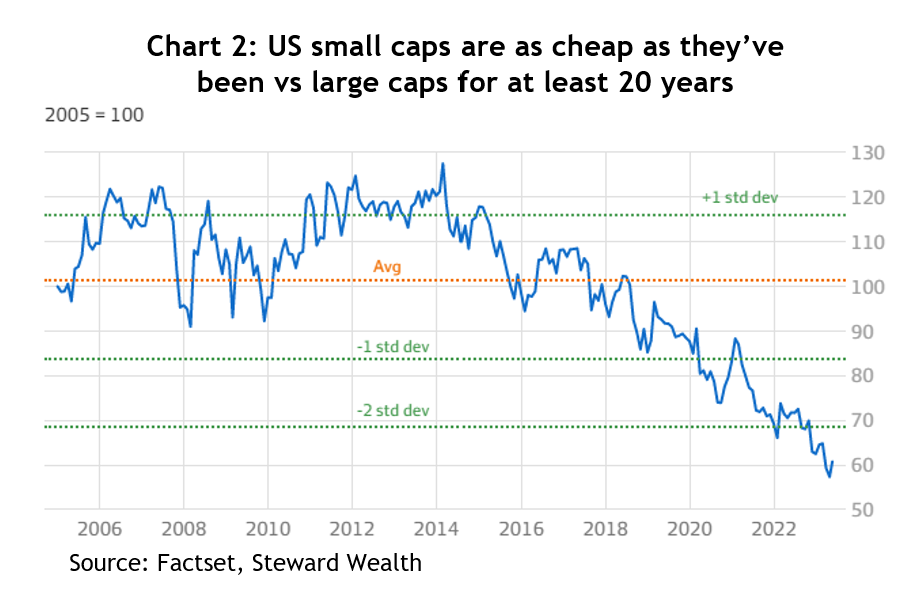
What is of far greater significance, though, is the valuation gap that’s opened up between US small cap companies and their large cap peers. When you compare their PE ratios, small caps are the cheapest they’ve been versus large cap stocks for well over 20 years and are now 2.5 standard deviations below the 20-year average – see chart 2, putting it in the 99th percentile.
Luke McMillan, Head of Research for one of Australia’s best performing small cap fund managers, Ophir, points out that, unlike the GFC where markets fell because earnings collapsed, the current market correction is largely due to investor sentiment turning sharply negative, which gets reflected in a drop in the PE (price to earnings) ratio.
Not unusually, when the market experiences a sentiment driven correction, referred to as ‘PE compression’, small caps companies get hit harder than large caps as investors opt for the perceived safety of bigger companies.
And that can be the rub with investing in small cap companies. While it’s easy to get excited by the runaway small cap success stories that made early investors rich, like Afterpay or REA Group, there are far more stories of investors that have either lost everything or have watched their investments go nowhere year after year. The annualised volatility of the Small Ordinaries index is 25 per cent higher than the ASX100, in other words, investors need to be prepared to buckle up for a bumpy ride.
Many small cap companies have either no analysts covering them or very few, so getting your hands on reliable information can be difficult, especially if the company’s based overseas. That can make for great opportunities for those investors capable of picking apart a cash flow statement and balance sheet, and who are prepared to put in the time and effort to get to know a company in detail and spot the gems before the crowd. But, as McMillan says, a great small cap company needs a lot more than a good story; smart management and strong financials are critical.
While fund managers can find it a real challenge to beat large cap indices, making passive investing via an ETF an attractive option, because of the huge dispersion between profitable and loss-making small caps, it’s usually much easier for a good manager to beat the small cap index. The trick is finding those good managers.
The final thing any smart investor needs to remember when investing in a riskier asset like small caps, is to size the investment appropriately for both their portfolio and, importantly, their risk appetite.